In This Article we discuss about universe comparison and the size of the universe, mainly the main focus on Size Of The Universe.
What is the size of the universe?
Our universe was according to us very small in size or at least this was our guess up-till a few hundred years before. The first thing we thought the Earth is at the center of our universe. But then we took out the Earth from the center as Copernicus did the Sun took its place. The idea was there is the Sun planets are present around it and after that are the stars and this is the whole universe now how many stars.
If you go to a very dark place and see the stars with your naked eyes, without a telescope you will think that you are seeing innumerable stars, but this is not so. you can see less than 10,000 stars only with your naked eye. This was in the sense the size of our universe.
But even hundred years before (by that time good big size, telescope had been invented) The idea is that our own galaxy Milky Way, which we call today as only one galaxy was the whole universe.
Today we know our Milky Way galaxy is quite big. There are 2-Hundred billion stars in it. And out of that our sun and its solar system is only one star. When astronomers Saw through a telescope Hundred years ago they observed a little fuzzy things on the sky they said these are spiral nebulae. But it was assumed that these spiral nebulae are a part of our galaxy they said these are spiral nebulae.
But it was assumed that these spiral nebulae are a part of the galaxy and our galaxy Milky Way in the whole universe. Then some astronomers (Edwin Hubble, specially comes to mind)
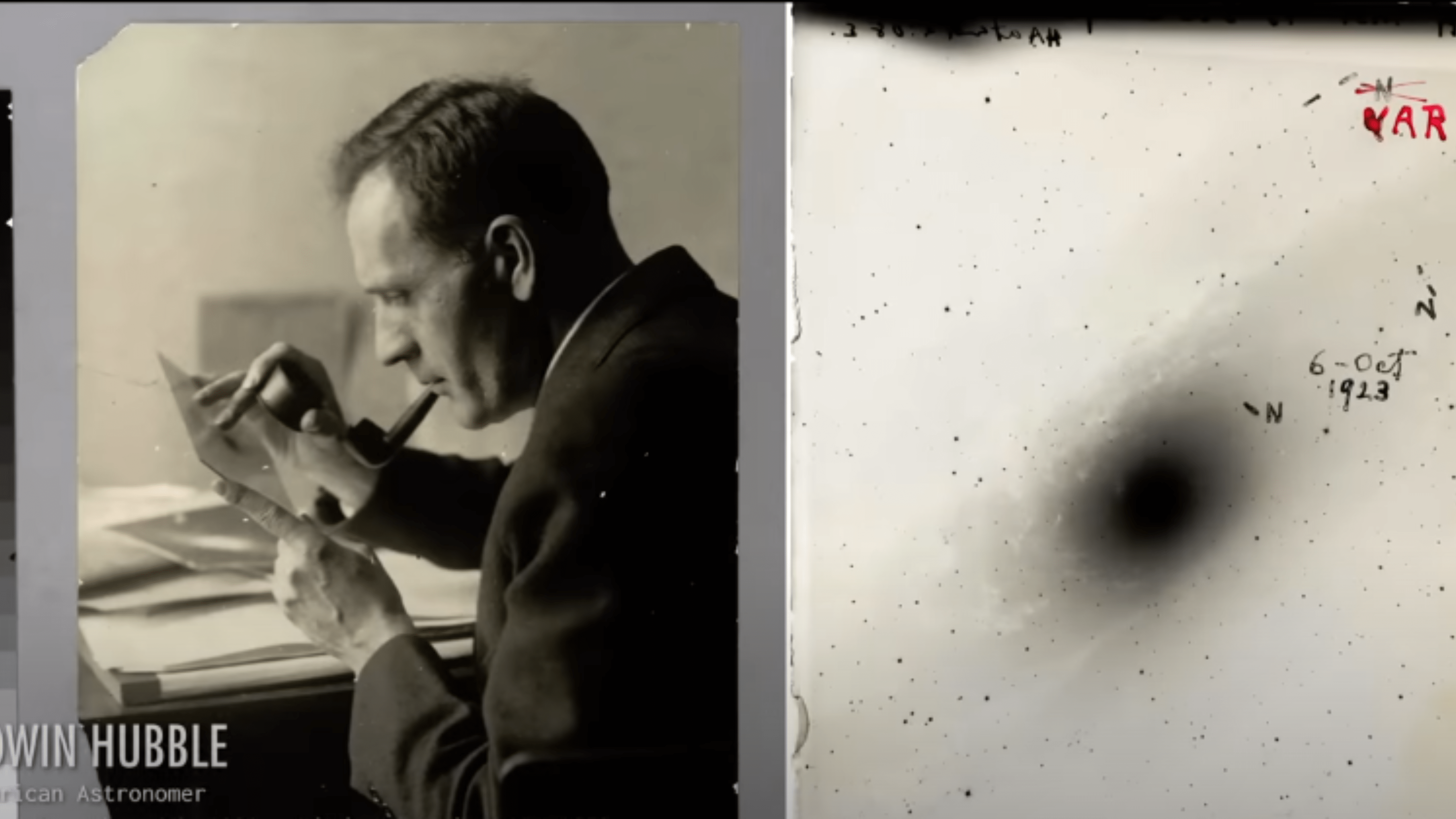

said when the distance of these spiral nebulae where measured it was learned that these itself were galaxies. They look small to us because they are very very very far away from us. From here around 1930 century, suddenly it came to be known that our universe is not only our galaxy, which has 200, billion stars in it. But it is much bigger than that, because these small spiral nebulae that could be seen (in which the most famous is Andromeda Galaxy)

Are like our galaxy in which there are hundreds of billions of stars. And they are very far that is why they look small.
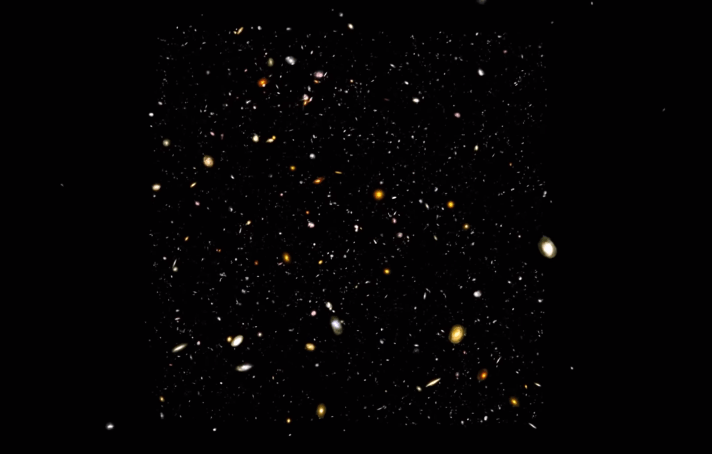
And so in the middle of the 20th century, we started knowing that our universe is full of galaxies, in fact, when we talk about of the universe today we say there are at least more than hundred billion galaxies and more than hundred billion stars in each galaxy. Now in a sense, you can say that stars are innumerable still one question arises, okay, this universe is very big but how big.
This question is difficult question conceptually because we are often used to talking about is inside our universe. When we start talking about the universe, a lot of our assumptions do not work. For that will be needing a little patience, it is a difficult topic. Regarding that let’s do this here I will go to explanations on how to tackle this question. How big is the universe end? At the end of this article I will summarise the answer if someone asks you, how big is the universe to this question.
We can trace back the beginning of our universe, normally up to 13800,000,000 years ago, which we call big bang. For this check another article on Big Bang, the evidence for the Big Bang. I want to clarify one or two, things about it. In spite of its name Big Bang this was not an explosion.
Neither it is, or as said, and people imagine, such a point where there was infinite density, in fact, astronomers or scientist (physicists) trace it back to search a time where is the density of the universe was very very very high.
In fact, it was so high you would have been able to fit the mass of hundred billion galaxies into a nucleus sized area of our universe. This is called by scientist ‘PLANCK DENSITY’.
Similarly, the universe at that time was very hard, its temperature was 100 million trillion trillion degrees. If you want to write it out, 1 and after that 32 zeros like this 100000000000000000000000000000000. This was the temperature of the universe this is called ‘PLANCK TEMPERATURE’. Astronomers know at that time the universe was expanding very rapidly. Why was it expanding? We do not know.
Now you will ask one minute what was happening before this density. Our laws do not tell us what was happening before Planck density because our physics in a sense break down and people are searching for what is called a quantum theory of gravity.
The idea is if more theories are form then we can explore what was before this Plank density but as of today, then astronomers scientists talk about the Big Bang, they talk about this hot dense place where 13.8 billion years ago this universe was expanding very rapidly.


Rather it expanded hundreds of millions of million times more than the speed of light. Now you will say one minute, nothing can travel faster than light. This very rapid expansion for a brief period is called inflation by astronomers, and after that the universe kept expanding at a modest speed. Expansion was taking place, but it was not inflation type. And as our universe kept expanding and as you can expect it’s temperature kept on decreasing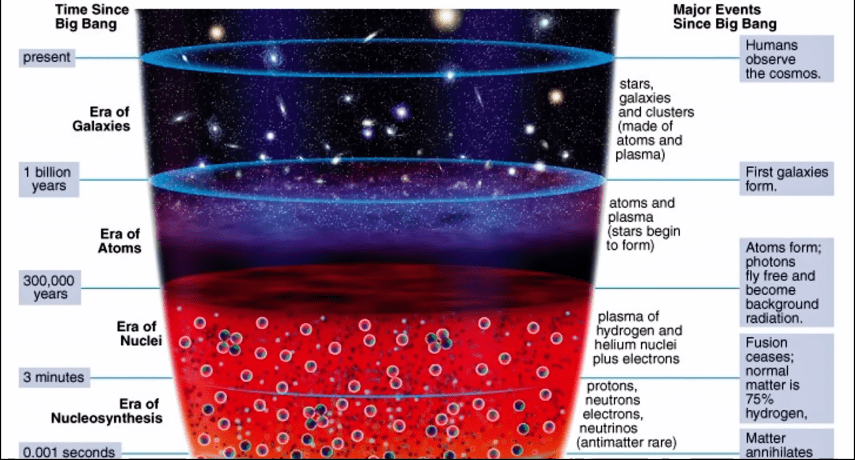
and it allowed quirks two form from energy into initial high temperatures period and after quirks electrons, protons, and neutrons with their combination and then read in a few minutes, after the beginning of our universe, most of hydrogen nucleus. Which is only proton and helium, which has two protons and two neutrons was formed.
And our universe kept on expanding its temperature kept big decreasing but we cannot see the time because the light then could not escape due to the high density meaning if a light photon and started to travel, it would suddenly collide with an electron or proton it was opaque (the universe).
But 400000 years later the temperature of our universe became so less that it is for the first time, the electrons which were moving freely until then got an opportunity to combine with the nuclei to form atoms.
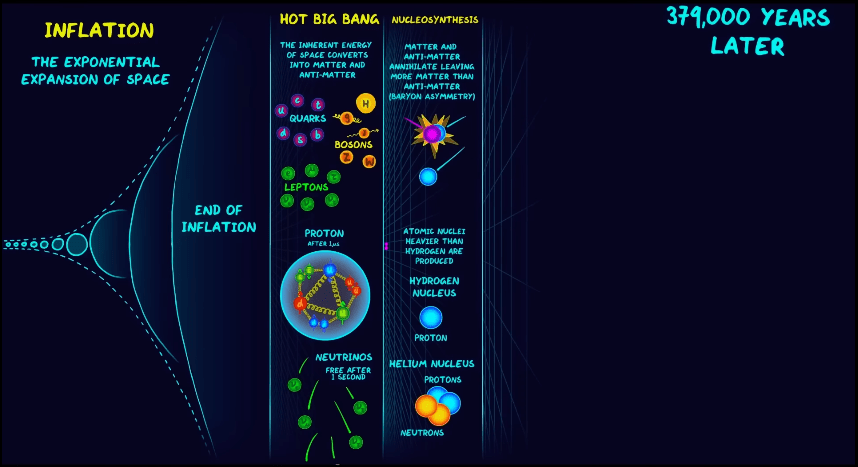
And when this electron became hydrogen and helium atom, and some lithium and beryllium for the first time light got a chance to move. This was a very specific prediction of the Big Bang model and its prediction was.

If we see in any direction this is called background radiation. We can see the life which came out for the first time after 400,000 years in every direction, and it is assumed due to the expansion of the universe. The temperature of that light is 3°K meaning it will be very cold.
In 1965, this specific prediction of big bang came to and when astronomers scientists detected it they came to know that actually the Big Bang model is correct and its biggest prediction proved to be correct.
In fact, this scientist, Arno Penzia and Robert Wilson, got the Nobel prize also in 1970. And you can imagine the universe kept expanding event after that and about and 200 million years after the Big Bang may be the first start formed and the first galaxies started forming.
When we talk about this James Webb space telescope this is in search of those first galaxies and first stars.

When was the first time, the universe kept expanding atoms, started forming after 400000 years universe further expended in some areas which were dense galaxies formed and inside the galaxies stars and with the stars planet, we came very late.
Our own solar system, our Milky Way (Milky Way was formed 12 billion years before) but our own solar system that is 5 billion years rather 4.5 billion years old. We came a lot of time after the Big Bang.
Okay, the story of the formation of the Sun and earth is different. We will talk about it some other time, but what about the question how big is our universe.
Some tricky things start here. As I said, we know that the big bang took place finite in time before 13 8 billion years ago. Then you can imagine that the light of some galaxy (if we see very far) which started travelling 13.8 billion years before is reaching us.
This is at the edge of the universe, we are seeing very far off the light from that galaxy started travelling 13.8 billion years ago and reached us today. But the universe during that period has been expanding. So this galaxy (who is light started 13.8 billion years ago and was received by us today) has gone further away in 13.8 billion years.
And according to calculation by astronomers, that galaxy today is almost 46,000,000,000 light years away from us. In a sense, you can think that we are seeing at a distance of 46 billion light years in every direction because that light of those galaxies is reaching us today, which started 13.8 billion years ago. This thing is called observable universe by astronomers meaning this is that universe, which we can see
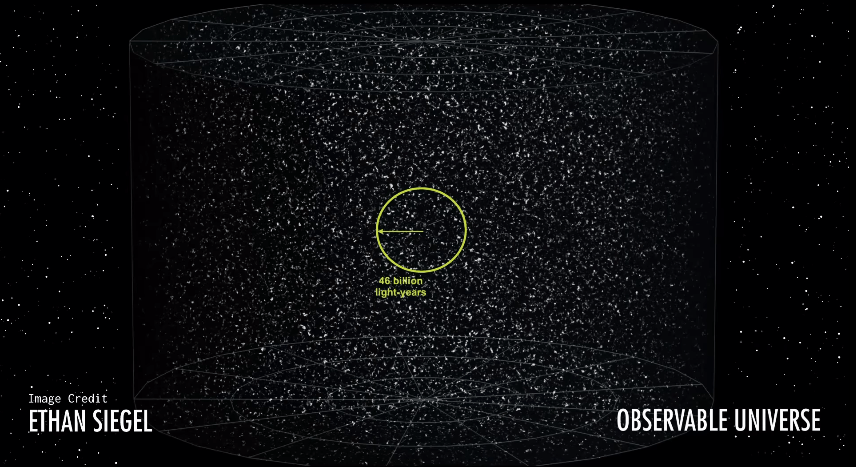
Right, are you still with me. This is the observable universe now if you ask this question. Is it possible for us to see a galaxy which is hundred billion light-years away from us?
No, the reason is the time when its light started travelling is more than the time of our universe meaning that are glad to see which is hundred billion light years away from us, it’s light will take hundred billion years to reach us.
But our universe is only 30 billion years old, so we have to wait for the light of that galaxy. Now you will say is it possible that galaxy is at a distance of hundred billion light-years. Definitely possible, rather our guess is our universe is even bigger than that but we cannot see that galaxies hundred billion years because its lights has not reached us yet.
This is the most tricky concept because the age of the universe is finite as I said 13 .8 billion years but its size is independent from its time. Be careful. I am saying it again. In this concept, that age of our universe is finite 13.8 billion years, but its size is not linked to its age.
It can be very big and it can be infinite also. Let’s talk a little more about it a few among you must be raising a question that we cannot see beyond the observable universe. How do we know it will not be different. Nothing stops is outside of the observable universe there may be a different universe, but in astronomy, there is concept called cosmological principle.
Its, foundation is (it started in Copernicus era) and it’s basic foundation is that we take the earth sun or our galaxy are not on a unique place.
In this way, people apply that beyond our observable universe, who is the radius is 40 billion light years or whose diameter is 92 billion light years
There is the same type of universe. As our observable universe will uncover it. We will come to know that there are also galaxies have been distributed the same way, as in our observable universe.
And other way to think about it is if you are on another galaxy (no matter how far) the diameter of their observable universe will be the same that is, it will be 92 billion light years. But it will be different from ours because they are farther away from us. When they make a circle, it is different. But the idea of the astronomers is, and this isn’t, as I’m sure that the universe beyond the observable universe is the same overall, as it is inside the observable universe.
And one wait to see the area beyond our observable universe is to keep waiting. If some galaxy is at a distance of hundred billion light years, we will know about it after waiting 100 billion years. But on a human scale this expansion of hundreds of years, thousands of years really does not tell us much with reference to billion of years. But this question still remains what is the size of our universe how big is that whole universe, which is beyond our of observable universe?
This is a very tricky problem, because we do not know even this our universe is Finite or infinite. And a conceptual problem arises here. If our universe was finite before

It means it will always remain finite. We do not know of any physical process which makes a finite thing infinite. Similarly, in reverse if our universe was infinite at the beginning, then it will always remain infinite. We do not know of any physical process, which makes an infinite thing finite.
I admit that these are very confusing type of concepts. Now Planck density from where this conversation of the universe began what was the size of the universe or whatever you call it before Planck density?
We do not know, but there are some matters by which these can be tested and astronomers have actually perform these tests. One thing is (and we will talk about the detail at some other time) this is in a way about geometry. The general theory of relativity tell us the geometry in our universe, which tells that if you want to see angles of a triangle, there is no need, it should be Euclidean geometry.
Euclidean geometry wars (the geometry, which is around the Earth) if you have a triangle of three angles should be 180°. but general theory of relativity allows that there can be such geometry (of the universe also) in which if you take the three angle of a triangle, it may be less than 180 or more than 180 these different types of geometry allow us, and then we can find out what we can say about the shape of our universe.
When astronomers measured
this thing,
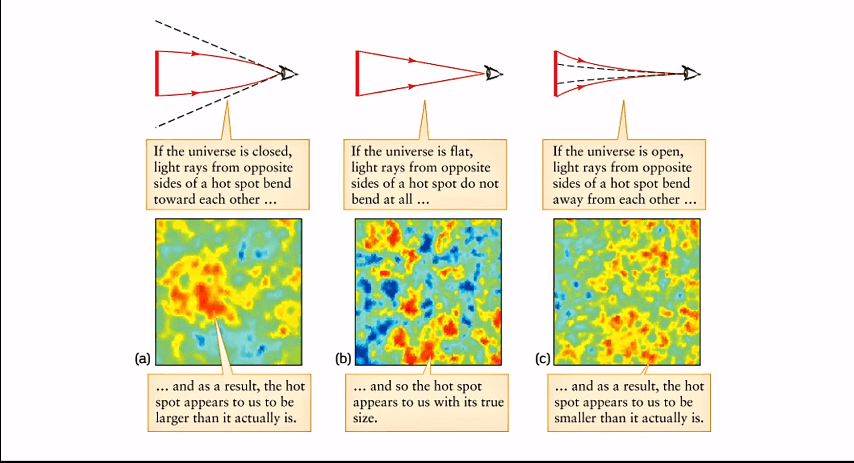
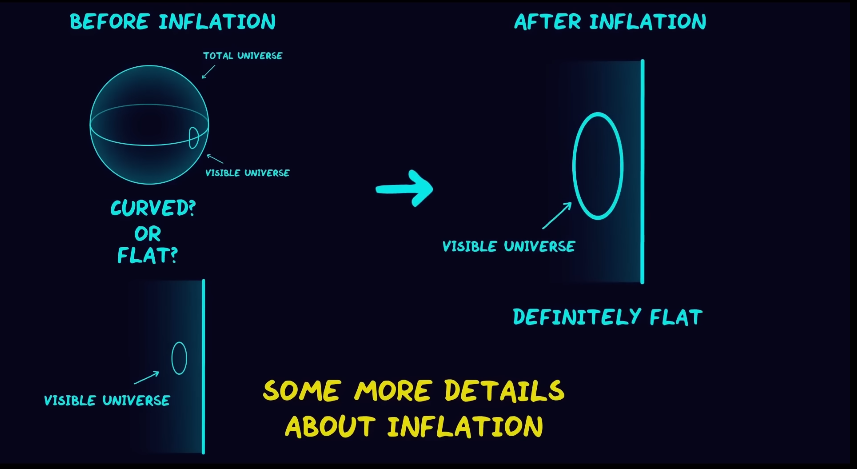
(And one way of measuring is, we mentioned the universe cosmic microwave background is related to that), they came to know that the geometry of our universe is in a way flat meaning if you make a big triangle of different futures, of cosmic microwave background (it is complicated how people measure it) it’s total is 180°.
Now this flatness, (astronomers, can it flat universe) in a way you will say that our universe is infinite. It is possible. But this is also possible that our observable universe (the universe you can see)
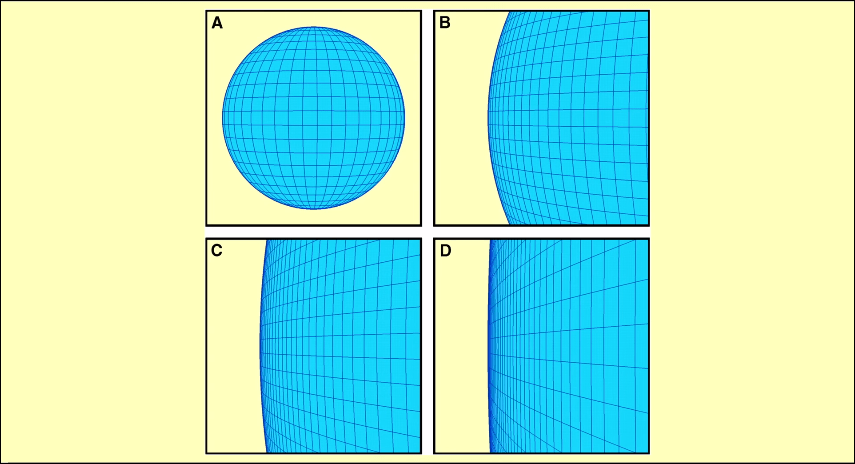
Is born, such a huge spherical universe, that the part on the edge we are present doing measurements looks like a flat universe. In that area if you take its analogue, the ball over there is so big that when we measure triangle on it, it’s sum is 180° according to Euclid. If this is true, that, our universe is very big, but it is not infinite then we can say that it is least several hundred times bigger than the observable universe (remember whose diameter is 92 billion light years).
But this is possible that our universe is infinite. Remember it is infinite has always been infinite. It is very difficult to imagine this thing because our minds cannot imagine infinity. If you ask me, I will say, it would be better if our universe is finite because then I can make you understand in a better way.
See our universe is very big but can observe a little piece of it but overall it is finite and we can measure its size. But this is possible that it may be infinite. Then the conversation about it will be different. The problem is whatever I may want this universe is not bound by my preference.
Right, we have reached the end of this long journey. Now we come to watch that question is somebody ask you what is the size of the universe how big is it. The correct answer is ‘do not know’.

several hundred billion universe are present which is called Multiverse, or are this universe, infinite a number. Maybe you will have to wait for the answer to these questions if we try to find them, but think for a minute.

We know that our observable universe is 92,000,000,000 light years across and we also know that the part of the universe on which we are now, was 13.8 billion years ago very dense and very small.

I think is an amazing achievement considering, that hundred years before we did not even know that there are other galaxies outside our Milky Way. So just imagine what would we be knowing after hundred years

