Eta Carinae is supermassive star. Our sun is an ordinary star. It is very special for us but related to the universe it is an ordinary star. Its end will be in an ordinary way. 99% of the stars in our universe are like our sun. But some stars are huge mass wise. Their mass is 8 times, 10 times or even more than the mass of our sun. The end of these stars is dramatic which is called supernova. We have an amazing opportunity to study a star before supernova. The name of this star is ‘ETA CARINAE’.
Eta Carinae and its Brightness
In 1677 astronomers cataloged a star in the southern hemisphere in constellation ‘CARINAE’. This was a dim star but after 1700, slowly slowly it started brightening up and after 1830, its brightness increased significantly rather, from 11th to 14th March 1843, it was the second brightest star in the sky. Its brightness was even more than ‘Rigel’, the start of the Orion constellation.
It seemed that this star had become a supernova but no, it kept on dimming for the next 50 years. This star is ‘Eta Carinae’.

This big increase in its brightness and then dimming again without exploding is called ‘Supernova imposter’ by astronomers, meaning this was not a supernova because the star was present after that but this increase and decrease in its brightness is, supernova imposter.
Story of Eta Carinae
We are not used to these big changes of brightness in the stars but this story is about a very interesting star. The ‘Eta Carinae’ is 7500 light years away from us. This star is so important that out of the key missions of the Hubble stethoscope, one mission was study Eta Carinae and find out what is happening to it and what is tells us about the evolution of stars.
Eta Carinae (its short form is Eta Car, easy to say) is in a star forming region like the Orion nebula where new stars are forming. Similarly, this Carina nebula is a star farming region and the different structures made in it, because of the formation of new stars and the death of big stars. If you observe Eta Carinae closely you win note this is not a normal star.
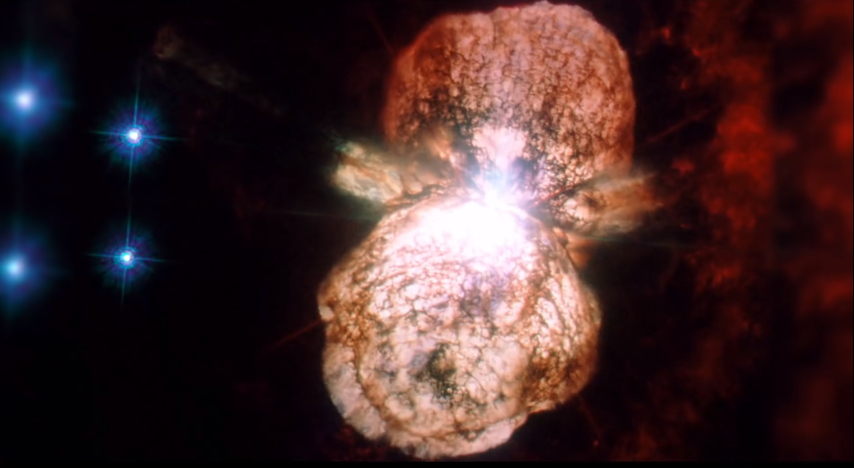

You can see two lobes in it and this is a dumbbell-type structure. Astronomers call it “HOMUNCULUS NEBULA”.
This two lobe structure you are seeing is the result of the 1843 eruption. Eta Carinae has 150 times more mass than our sun. Astronomers think this the most massive star of our milky way galaxy.
The idea is that in the 1843 eruption, it ejected 10 percent of its mass and the double lobe feature we can see today is that mass ejection or the result of that eruption.
Eta Carinae LBV
These stars such as Eta Carinae have a short life. The specific classification of Eta Carinae ‘LUMINOUS BLUE VARIABLE’ or (LBV) by astronomers. To understand this star properly astronomers used different type of wavelengths or different lights.

This is very common in astronomy that whenever we try to understand something, we have to see it not only in visible light but also in other wavelengths such as infrared, x-rays etc.
Material of Eta Carinae Still expanding
Astronomers have been observing the material of this double lobe structure for sometime and found that it is still expanding. Remember this eruption took place in 1843 and this material is still expanding very fast, the speed is 600 times the speed of a rifle bullet.

You are seeing a little ultraviolet light with this double lobe structure. These big stars emit a lot of ultraviolet light. The ultraviolet light (blue) you are seeing in the middle of the lobes, in the picture are look like rays.

The red thing you are seeing is Hydrogen gas. Which has been ionized by ultraviolet light of Eta Car and is a specific signature that Ah extremely hot light is present. This is hydrogen light (Red).

The purple color you see in the image by Chandra space telescope in x-rays. This x-ray gas is actually the material of the outburst of Eta Carina, which is now colliding with some other material.
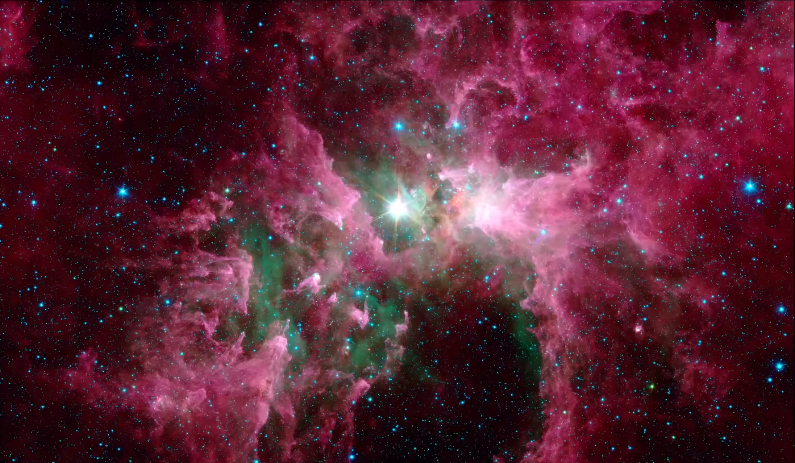
This is its infrared image and Eta Carina is very bright in infrared. It is the brightest source of infrared in the whole sky.
Eta Carina binary system
The astronomers think that actually this Eta Carina or Eta Car is not a solitary star, it is a part of a binary star system. And this second star is also not a small star. It is quite big. Eta Car is probably the most massive star of our galaxy. Its mass is 150 times more than the mass of our sun.
The secondary star in this system is 30 times bigger than our sun. These two stars are making a binary system. This is a strange system because the outbursts of Eta Car are also moving with it.
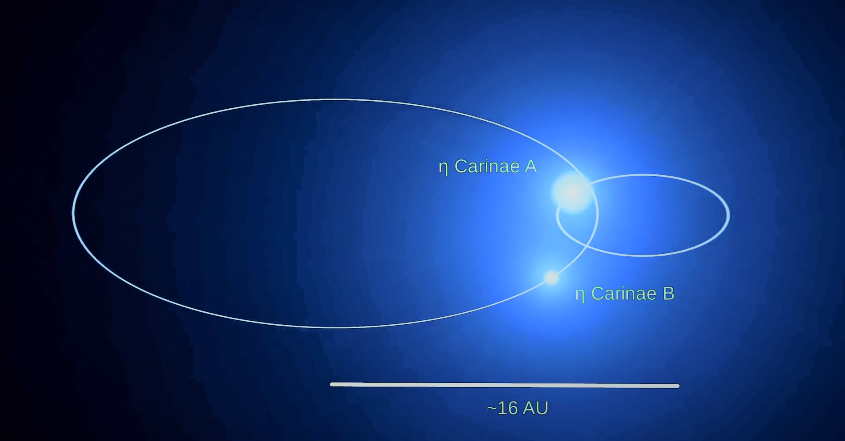
Astronomers have calculated that it takes five and a half years for the stars of this system to complete an orbit around one another. And the average distance of the secondary star from the primary star (Eta Car) is approximately 15 astronomical units. This is the distance of the middle point of Saturn and Uranus from our sun. This is the distance between these two stars.
The idea is this secondary star is probably stuck up in the winds of Eta Car and maybe there is a small accretion disc around it because of Eta Car. Maybe because of this the material cannot eject from the equator in the middle and this double lobe structure is formed.
Supernova of Eta Carinae
Eta Carinae is an interesting star. Many fluctuations are taking place in it. The supernova imposter also happened in its lifetime relatively is also less, then when will it be a supernova? They estimate of astronomers is that this start will be a supernova in a few hundred thousand years abd another good thing is that it is so far from that no harm will come to earth and there will be no effect on earth.
But it will look magnificent in the sky, and the idea is, this will be the brightest supernova in our recorded history. It is assumed that when Eta Car, because of its distance and because it’s a big star become a supernova it will look much brighter than Venus from the Earth. It may be visible at day time also.

